Obesity in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Obesity
means your child's body mass index (BMI) is at or above the 95th percentile. BMI is your child's weight divided by height. The percentile compares your child's BMI with the BMIs of children his or her age.
The risks of obesity include:
- Low self-esteem, being bullied, depression, or eating disorders
- Diabetes
- Heart disease, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol
- Asthma and sleep apnea (episodes in which your child stops breathing at night)
- Arthritis, knee, and hip pain
- Gallbladder and liver disease
- Abnormal monthly periods and other hormone problems
- A higher risk for obesity as an adult
Seek care immediately if:
- Your child has a severe headache or vision problems.
- Your child has trouble breathing during physical activity.
Call your child's doctor if:
- Your child has lost interest in social activities, does not want to go to school, or seems depressed.
- Your child has signs of diabetes, such as being very hungry, very thirsty, and urinating often.
- Your child has signs of gallbladder or liver disease, such as pain in the upper abdomen.
- Your child has hip or knee pain and discomfort while walking.
- Your child has signs of sleep apnea, such as daytime sleepiness, snoring, or bed wetting.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Treatment for obesity
focuses on decreasing your child's BMI and risk for health problems. In some cases, your healthcare provider may suggest that your child maintain the current weight. As your child grows in height, the BMI will decrease. Even a small decrease in BMI can reduce the risk for many health problems. Your child's healthcare provider will work with you and your child to set a weight-loss goal.
- Meet with other healthcare providers to help you and your child start to make lifestyle changes. Other providers may include a dietitian, physical therapist, and psychologist.
- Lifestyle changes include making healthy food choices and getting regular physical activity.
- Other treatments may be suggested by your healthcare provider if your child is older and has medical problems caused by obesity. These treatments are used in addition to lifestyle changes to treat severe obesity. Medicine may be given to decrease the amount of fat your child's body absorbs from food.
Eating changes your family can make:
 |
- Stick to a schedule of 3 meals a day and 1 or 2 healthy snacks. Meals and snacks should be 2 to 4 hours apart. Only offer water between meals.
- Eat dinner together as a family as often as possible. Ask your child to help you prepare meals. Limit fast food and restaurant meals because they are often high in calories.
- Decrease portion sizes. Use small plates, no larger than 9 inches in diameter. Fill your child's plate half full of fruits and vegetables. Do not put serving dishes on the table. Do not make your child finish everything on the plate.
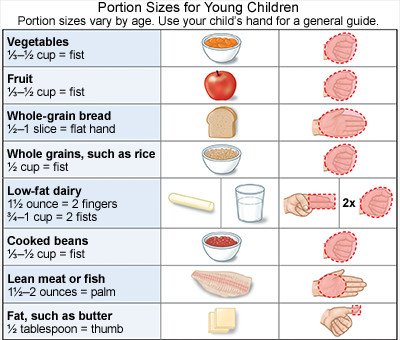
- Limit soda, sports drinks, and fruit juice. These sugary beverages are high in calories. Offer your child water as the main beverage.
- Pack healthy lunches. An example is a turkey sandwich on whole-wheat bread with an apple, baby carrots, and low-fat milk.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Activity changes your family can make:
- Encourage your child to be active for 60 minutes most days of the week. Find sports or activities that are fun for your child, such as cycling, swimming, or running. Be active with your child. Go for a walk, go bowling, or play at a park.
- Limit your child's screen time. Screen time is the amount of television, computer, smart phone, and video game time your child has each day. It is important to limit screen time. This helps your child get enough sleep, physical activity, and social interaction each day. Your child's pediatrician can help you create a screen time plan. The daily limit is usually 1 hour for children 2 to 5 years. The daily limit is usually 2 hours for children 6 years or older. You can also set limits on the kinds of devices your child can use, and where he or she can use them. Keep the plan where your child and anyone who takes care of him or her can see it. Create a plan for each child in your family. You can also go to https://www.healthychildren.org/English/media/Pages/default.aspx#planview for more help creating a plan.
- Help your child have a regular sleep schedule. Make sure your child gets at least 8 hours of sleep each night. Sleep schedules that are not consistent can affect your child's weight.
How you can help your child:
- Set small, realistic goals. An example of a small goal is to offer fruits and vegetables at every meal.
- Teach your child how to make healthy choices. This includes when your child is at school or away from home. Praise your child for healthy choices. Do not talk about diets or weight. Do not allow teasing in your home.
- Do not use food to reward or punish your child. Reward your child with fun activities or social events with friends.
- Try not to bring chips, cookies, and other unhealthy foods into your home. Ask your child to help you make healthy choices while grocery shopping. Shop for healthy snacks, such as fruit, yogurt, nuts, and low-fat cheese.
Follow up with your child's healthcare providers as directed:
Your child may need weight check follow-up visits. You and your child may need to meet with a dietitian. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Obesity
- Can You Mix Weight Loss Drugs and Alcohol?
- FDA-Approved Weight Loss Drugs: Can They Help You?
- How to Calculate Your Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Side Effects of Weight Loss Drugs
- Surgery for Weight Loss: What Are Your Options?
- U.S. Childhood Obesity Epidemic: Treatment and Prevention
- Weight Loss Drugs: What Are Your Options?
- Which Drugs Cause Weight Gain?
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
