Obesity
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Obesity
means your body mass index (BMI) is greater than 30. Your healthcare provider will use your age, height, and weight to measure your BMI.
The risks of obesity include
many health problems, including injuries or physical disability.
- Diabetes (high blood sugar level)
- High blood pressure or high cholesterol
- Heart disease or heart failure
- Stroke
- Gallbladder or liver disease
- Cancer of the colon, breast, prostate, liver, or kidney
- Sleep apnea
- Arthritis or gout
Screening
is done to check for health conditions before you have signs or symptoms. If you are 35 to 70 years old, your blood sugar level may be checked every 3 years for signs of prediabetes or diabetes. Your healthcare provider will check your blood pressure at each visit. High blood pressure can lead to a stroke or other problems. Your provider may check for signs of heart disease, cancer, or other health problems.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have a severe headache, confusion, or difficulty speaking.
- You have weakness on one side of your body.
- You have chest pain, sweating, or shortness of breath.
Call your doctor if:
- You have symptoms of gallbladder or liver disease, such as pain in your upper abdomen.
- You have knee or hip pain and discomfort while walking.
- You have symptoms of diabetes, such as intense hunger and thirst, and frequent urination.
- You have symptoms of sleep apnea, such as snoring or daytime sleepiness.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment for obesity
focuses on helping you lose weight to improve your health. Even a small decrease in BMI can reduce the risk for many health problems. Your healthcare provider will help you set a weight-loss goal.
- Lifestyle changes are the first step in treating obesity. These include making healthy food choices and getting regular physical activity. Your healthcare provider may suggest a weight-loss program that involves coaching, education, and therapy.
- Medicine may help you lose weight when it is used with a healthy foods and physical activity.
- Surgery can help you lose weight if you have obesity along with other health problems. Several types of weight-loss surgery are available. Ask your healthcare provider for more information.
Tips for safe weight loss:
- Set small, realistic goals. An example of a small goal is to walk for 20 minutes 5 days a week. Anther goal is to lose 5% of your body weight.
- Ask for support. Tell friends, family members, and coworkers about your goals. Ask someone to lose weight with you. You may also want to join a weight-loss support group.
- Identify foods or triggers that may cause you to overeat. Remove tempting high-calorie foods from your home and workplace. Place a bowl of fresh fruit on your kitchen counter. If stress causes you to eat, find other ways to cope with stress. A counselor or therapist may be able to help you.
- Track your daily calories and activity. Write down what you eat and drink. Also write down how many minutes of physical activity you do each day.
- Track your weekly weight. Weigh yourself in the morning, before you eat or drink anything but after you use the bathroom. Use the same scale, in the same place, and in similar clothing each time. Only weigh yourself 1 to 2 times each week, or as directed. You may become discouraged if you weigh yourself every day.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Eating changes:
You will need to eat 500 to 1,000 fewer calories each day than you currently eat to lose 1 to 2 pounds a week. The following changes will help you cut calories:
- Eat smaller portions. Use small plates, no larger than 9 inches in diameter. Fill your plate half full of fruits and vegetables. Measure your food using measuring cups until you know what a serving size looks like.
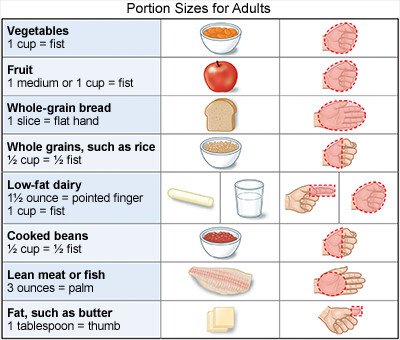
- Eat 3 meals and 1 or 2 snacks each day. Plan your meals in advance. Cook and eat at home most of the time. Eat slowly. Do not skip meals. Skipping meals can lead to overeating later in the day. This can make it harder for you to lose weight. Talk with a dietitian to help you make a meal plan and schedule that is right for you.
- Eat fruits and vegetables at every meal. They are low in calories and high in fiber, which makes you feel full. Do not add butter, margarine, or cream sauce to vegetables. Use herbs to season steamed vegetables.
- Eat less fat and fewer fried foods. Eat more baked or grilled chicken and fish. These protein sources are lower in calories and fat than red meat. Limit fast food. Dress your salads with olive oil and vinegar instead of bottled dressing.
- Limit the amount of sugar you eat. Do not drink sugary beverages. Limit alcohol.
 |
Activity changes:
Physical activity is good for your body in many ways. It helps you burn calories and build strong muscles. It decreases stress and depression, and improves your mood. It can also help you sleep better. Talk to your healthcare provider before you begin an exercise program.
- Exercise for at least 30 minutes 5 days a week. Start slowly. Set aside time each day for physical activity that you enjoy and that is convenient for you. It is best to do both weight training and an activity that increases your heart rate, such as walking, bicycling, or swimming.


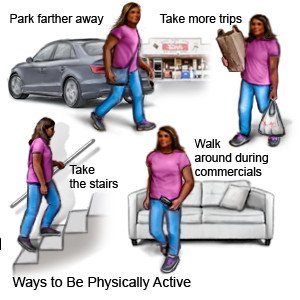
- Find ways to be more active. Do yard work and housecleaning. Walk up the stairs instead of using elevators. Spend your leisure time going to events that require walking, such as outdoor festivals or fairs. This extra physical activity can help you lose weight and keep it off.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
You may need to meet with a dietitian. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Obesity
- Can You Mix Weight Loss Drugs and Alcohol?
- FDA-Approved Weight Loss Drugs: Can They Help You?
- How to Calculate Your Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Side Effects of Weight Loss Drugs
- Surgery for Weight Loss: What Are Your Options?
- U.S. Childhood Obesity Epidemic: Treatment and Prevention
- Weight Loss Drugs: What Are Your Options?
- Which Drugs Cause Weight Gain?
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
