Coronary Artery Disease in Women
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is coronary artery disease (CAD)?
CAD, or heart disease, occurs when arteries that supply blood to your heart become narrow or blocked. CAD is caused by plaque (cholesterol, fat, and other substances) that builds up in your arteries. Oxygen cannot get to your heart when your arteries narrow or become blocked, which may be life-threatening.
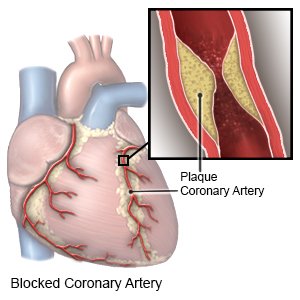 |
What increases my risk for CAD?
- Obesity and lack of exercise
- Poor nutrition
- Age 45 years or older
- High blood pressure or high cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Stress
- Smoking, or drinking alcohol
- Certain medicines, such as birth control pills
- Family or personal history of heart attack
What are the signs and symptoms of CAD in women?
You may not have any symptoms at first. Symptoms may begin slowly but increase quickly as plaque builds up in your arteries. You may not notice symptoms until the artery starts to become blocked. Women often do not have the common signs and symptoms that men tend to have. You may have any of the following:
- Chest pain or a tight, heavy, burning feeling in your chest
- Pain in your back, neck, stomach, or jaw
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Indigestion, heartburn, or loss of appetite
- Fast, slow, or pounding heartbeat
- Feeling more tired or weak than usual
- Anxiety
How is CAD diagnosed in women?
You may need any of the following:
- Blood tests will check for high cholesterol or other medical conditions that may have led to CAD.
- An EKG records the electrical activity of your heart. It is used to check your heart rhythm and it may show if there is damage to your heart.
- An echocardiogram is a type of ultrasound. Sound waves are used to show the structure, movement, and blood vessels of your heart.
- An exercise stress test helps healthcare providers see the changes that take place in your heart during exercise. An EKG is done while you ride an exercise bike or walk on a treadmill. Healthcare providers will ask if you have chest pain or trouble breathing during the test.
- A stress test with medicine may be done if you cannot do the exercise stress test. You are given medicine that makes your heart work harder. You will be connected to a stress test machine.
- An angiography, chest x-ray, CT scan, or MRI may be done to take pictures of your blood vessels and arteries. The pictures may show how narrow or blocked your blood vessels are. You may be given contrast liquid to help healthcare providers see the pictures better. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
Which medicines are used to treat CAD?
- Blood pressure medicines are given to lower your blood pressure. These medicines may include ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers. ACE inhibitors help keep your blood vessels relaxed and open. This helps keep blood flowing into your heart. Beta-blockers keep your heart pumping strongly and regularly. This helps keep your heart from working too hard to get oxygen.
- Cholesterol medicines help lower blood cholesterol levels.
- Nitrates , such as nitroglycerin, relax the arteries of your heart so it gets more oxygen. Nitrates may also help relieve your chest pain.
- Diuretics help your body get rid of extra fluid and protect your heart from more damage. You may urinate more often while you are taking diuretics.
- Antiplatelets , such as aspirin, help prevent blood clots. Take your antiplatelet medicine exactly as directed. These medicines make it more likely for you to bleed or bruise. If you are told to take aspirin, do not take acetaminophen or ibuprofen instead.
- Blood thinners keep clots from forming in your blood. Clots may cause heart attacks, strokes, or death. This medicine makes it more likely for you to bleed or bruise.
What are some other treatments for CAD?
Your healthcare provider will work with you to create a treatment plan. In addition to medicines, your provider may recommend a procedure or surgery to open your arteries. Your provider can explain the benefits and risks of each treatment. The following are commonly used to treat CAD:
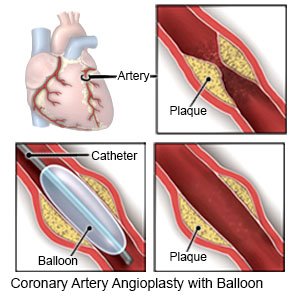
- An angioplasty may be done to open an artery blocked by plaque. A tube with a balloon on the end is put into the blocked artery. When the tube is in the artery, the balloon is inflated. As the balloon inflates, it presses the plaque against the artery wall to open the artery. A stent may be placed in your artery to keep it open.
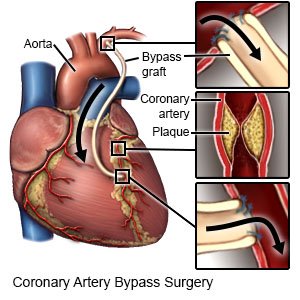
- Coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) is open heart surgery. Healthcare providers take arteries or veins from other areas in your body and use them to bypass or go around the blocked arteries of your heart.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What is cardiac rehabilitation?
Your healthcare provider may recommend that you attend cardiac rehabilitation (rehab). This is a program run by specialists who will help you safely strengthen your heart and prevent more heart disease. The plan includes exercise, relaxation, stress management, and heart-healthy nutrition. Healthcare providers will also check to make sure any medicines you take are working. The plan may also include instructions for when you can drive, return to work, and do other normal daily activities.
What can I do to manage or prevent CAD?
- Do not take certain medicines without asking your healthcare provider first. These include NSAIDs, herbal or vitamin supplements, or hormones (estrogen or progestin).
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause heart and lung damage. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Be physically active. Physical activity, such as exercise, can lower your blood pressure, cholesterol, weight, and blood sugar levels. Healthcare providers will help you create exercise goals. They can also help you make a plan to reach your goals. For example, you can break exercise into 10-minute periods, 3 times in the day. Find an exercise that you enjoy. This will make it easier for you to reach your exercise goals.

- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Your provider can help you create a healthy weight loss plan, if needed. A weight loss of at least 10% can improve your heart health.
- Eat heart-healthy foods. Heart-healthy foods include fresh fruits and vegetables, low-fat or skim dairy products, fish, chicken (without skin), and lean meats. Eat two 4-ounce servings of fish high in omega-3 fats each week, such as salmon, fresh tuna, and herring. Avoid foods high in trans fat, such as baked goods or fried foods.
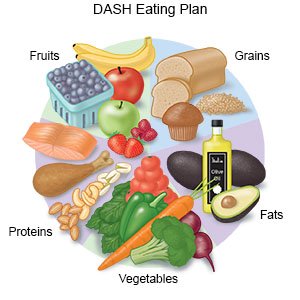
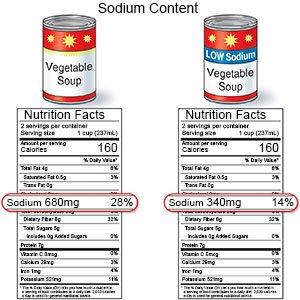
- Limit sodium (salt). Avoid foods that are high in sodium, such as canned foods, potato chips, salty snacks, and cold cuts. If you add salt while you cook, do not add more at the table.
- Limit or do not drink alcohol. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
- Manage other health conditions. Follow your healthcare provider's advice on how to manage other conditions that can affect your heart health. These include diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. You may need to take medicines for these conditions and make other lifestyle changes.
- Manage stress. Stress can raise your blood pressure. Find new ways to relax, such as deep breathing or listening to music.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. Your healthcare provider can tell you which vaccines you need, and when to get them. The following vaccines help prevent diseases that can become serious for a person with CAD:
- The influenza (flu) vaccine is given each year. Get a flu vaccine as soon as recommended, usually in September or October.
- The pneumonia vaccine is usually given every 5 years. Your healthcare provider may recommend the pneumonia vaccine if you are 65 or older.
- COVID-19 vaccines are given to adults as a shot. At least 1 dose of an updated vaccine is recommended for all adults. COVID-19 vaccines are updated throughout the year. Adults 65 or older need a second dose of updated vaccine at least 4 months after the first dose. Your healthcare provider can help you schedule all needed doses as updated vaccines become available.
 |
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone call if:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have chest pain that happens often.
- You have chest pain at rest.
When should I call my doctor?
- You feel depressed or anxious.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Coronary Artery Disease
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
